

When running a multi-faceted HR department, relying on instinct and guesswork to make critical decisions isn’t viable.
Are you ready to take your HR department to the next level and make data-driven decisions that drive business success? If so, HR analytics can provide you with the valuable insights you need.
HR analytics uses data and statistical methods to analyze and interpret human resources data, in key areas like employee turnover, productivity, and satisfaction. This powerful tool can help you identify areas of improvement, predict future trends, and optimize your talent management strategies.
There are four types of HR analytics. In this blog, we shall be exploring all the different types of HR analytics, from basic descriptive analytics to more advanced types of HR analytics like predictive and prescriptive analytics.
So, if you’re ready to unlock the full potential of your workforce and take your HR department to the next level, join us as we explore the exciting world of HR analytics.
Let’s get started with the most basic question:
HR Analytics, or Human Resources Analytics, is an important tool HR professionals use. HR Analytics is the process of analyzing and interpreting data related to a company’s workforce to gain valuable insights and make data-driven decisions.
This can include analyzing data related to key aspects of the company like employee performance, engagement, retention, recruitment, and other HR functions, and identify areas of improvement to enhance the company’s performance.
At its core, HR analytics uses data and statistical methods to identify patterns, trends, and correlations in key aspects of a company to help organizations optimize their talent management strategies, improve employee engagement and satisfaction, and ultimately gain success in the highly competitive market.
There are different types of HR Analytics that we shall discuss in detail later in the blog.
HR Analytics is an important aspect of business management because it provides organizations with valuable insights and deeper understanding of their workforce.
By HR data analysis, organizations can identify trends, patterns, and correlations related to employee performance, engagement, absenteeism, and retention, which can help them make data-based decisions that optimizes their talent management strategies.
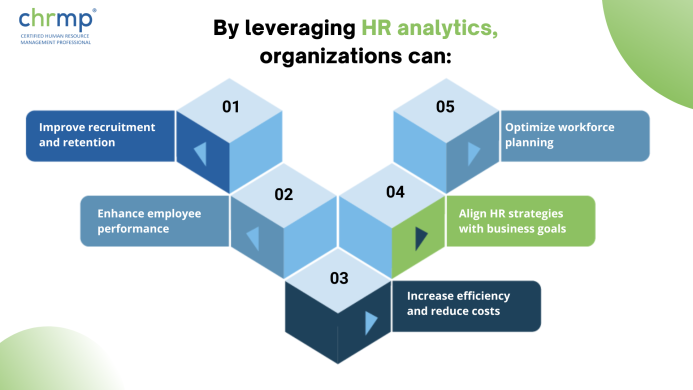
HR Analytics help organizations improve their recruitment, employee engagement and retention efforts while curtailing turnover rates and absenteeism. By analyzing data related to the employee lifecycle, organizations can identify improvement areas and adjust their recruitment and retention strategies to attract and retain top talent.
HR Analytics also help organizations optimize their performance management processes. By analyzing data related to employee performance, organizations can identify areas of improvement and adjust their performance management processes to drive better results for the organization as a whole.
Finally, HR Analytics help organizations align their HR strategies with their business goals. By using data to drive decision-making, organizations ensure that their HR strategies are aligned with their business goals, which usually drives business success to higher levels.
In summary, HR Analytics is important because it provides organizations with valuable insights, helps them improve their recruitment and retention efforts, curb absenteeism and turnover rates,optimize their performance management processes, and align their HR strategies with their business goals which also pushes up financial metrics.
HR analytics offers several benefits to organizations. Here are three key advantages of utilizing HR analytics:
1.Data-driven decision-making: HR analytics enables organizations to make informed decisions based on data and insights rather than relying solely on intuition or subjective judgments. By analyzing HR data, organizations can identify patterns, trends, and correlations that provide valuable insights into various HR processes and outcomes.
2. Improved recruitment and retention: HR analytics can significantly enhance recruitment and retention efforts. By analyzing data related to recruitment processes, organizations can identify which sourcing channels, assessment methods, or selection criteria are most effective in attracting and hiring high-performing candidates.
3. Enhanced workforce planning and performance management: HR analytics provides insights into workforce trends, skill gaps, and performance metrics, allowing organizations to proactively plan for their future workforce needs.
These benefits of HR analytics contribute to more effective HR management, alignment of HR practices with organizational goals, and ultimately, better business outcomes.
HR analytics is a rapidly growing field that has become increasingly important for organizations of all sizes. By using HR analytics, organizations can gain valuable insights into their workforce and make data-driven decisions to optimize their talent management strategies.
There are four types of HR analytics: descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics. Each analytics type has its unique purpose and can help HR professionals address specific workforce issues.
Here are the four types of HR analytics described in detail:
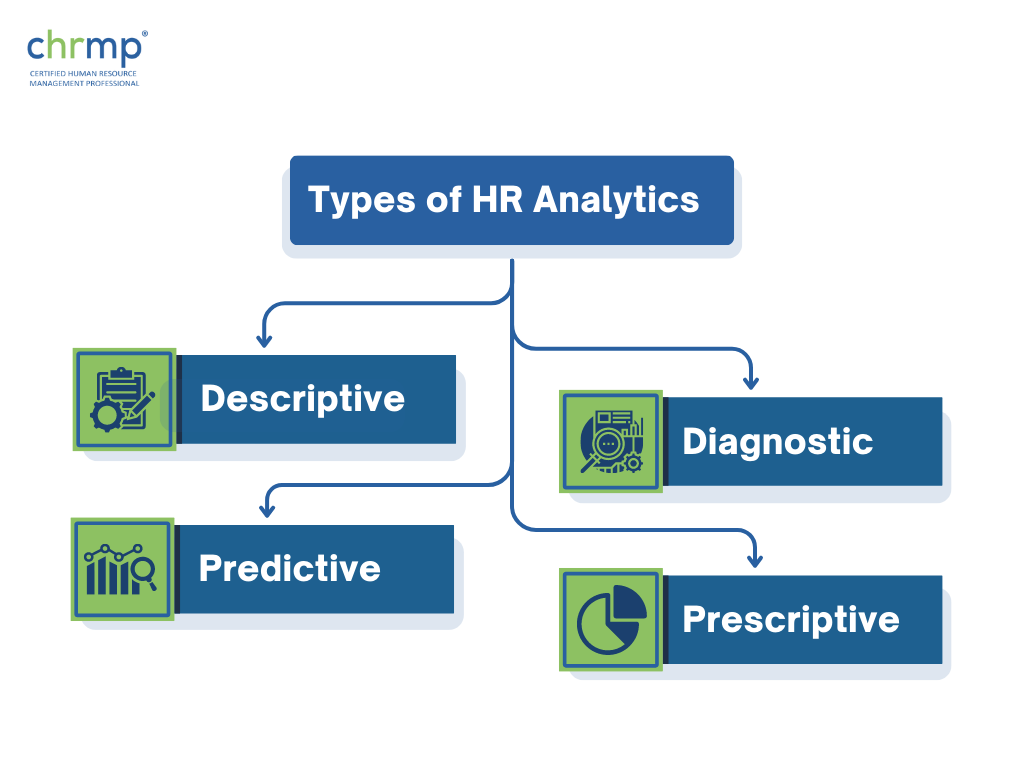
Descriptive analytics is a type of HR analytics that involves analyzing historical data to gain an understanding of what had happened in the past.
It summarises data that helps identify patterns and trends, such as employee turnover rates, absenteeism, or workforce demographics.
Descriptive analytics is an important tool for HR professionals to help them make sense of large amounts of data collected over the past years and identify areas of improvement.
Using descriptive analytics, HR professionals can answer questions such as: How many employees were hired last year? What was the average salary for a specific job role? How many employees left the organization and their absentieeism rate?
This information can be used to develop insights and identify areas where HR improvement or process optimization can occur.
Descriptive analytics provides a foundation for more advanced types of analytics, such as predictive extrapolative and prescriptive analytics, that can help HR professionals anticipate future trends and develop strategies to optimize their workforce performance.
Diagnostic analytics is an HR analytics that goes beyond the descriptive analysis of past events to identify the root cause of workforce problems or issues. It involves analyzing and extrapolating data to determine why certain trends or patterns are occurring in the workforce data. By examining historical data, diagnostic analytics can help HR professionals understand why certain events have occurred in the past years and what factors have contributed to their occurrence.
For example, if an organization is experiencing high turnover rates, diagnostic analytics helps them identify the problem’s underlying causes. It reveals whether the turnover is related to certain departments or job roles, and whether it’s due to poor management, lack of career development opportunities, or inadequate compensation and welfare amenities. Once the underlying causes are identified, HR professionals can address the issue and develop effective solutions to improve employee retention and engagement while curtailing sabbaticals and absenteeism.
Diagnostic analytics is a valuable tool for HR professionals which helps them identify and address workforce issues before they become more serious problems. Using diagnostic analytics, HR professionals can improve employee engagement and retention, leading to a more productive and successful organizational workforce.
Predictive analytics is a type of HR analytics that uses statistical algorithms, extrapolative methods and machine learning techniques to analyze historical data and predict future outcomes. It involves identifying patterns and trends in workforce data, then extrapolating using that information, to make predictions about future workforce behavior.
Predictive analytics can help HR professionals anticipate future workforce trends, such as employee turnover or skills gaps, and develop strategies to address them before they become major issues. Unless some major disruptive event takes place in the process, such extrapolative calculated outcomes generally hold true.
For example, predictive analytics can be used to develop models that predict which employees are most likely to leave the organization in the next year.
This information can be used to proactively identify and address the underlying causes of employee turnover, be it satisfactory compensation, lack of welfare amenities, growth opportunities etc. before it becomes a more serious problem.
Similarly, predictive analytics can be used to identify which employees are most likely to be promoted, providing insights into where to invest in training and development programs.
Predictive analytics is a powerful tool among the different types of HR analytics for HR professionals, allowing them to make data-driven decisions and develop strategies based on accurate data-predictions of future outcomes.
By using predictive analytics, HR professionals can improve their recruitment and retention efforts, optimize their workforce planning, and ultimately drive business success to greater heights
Prescriptive analytics is a type of HR analytics that works using data, algorithms, and machine learning techniques to recommend actions that HR professionals can take to optimize their workforce and curb negative phenomena involving the workforce from taking root.
It goes beyond predictive analytics, which predicts what might happen, to suggest what should be done to prevent it from occurring.
Prescriptive analytics uses statistical models to analyze data and recommend specific courses of action. It’s similar to a doctor’s prescription that gives preventive medicine to prevent some particular ailment from afflicting, metaphorically speaking.
For example, suppose a company is beginning to experience high employee turnover rates. In that case, prescriptive analytics can suggest specific strategies for addressing the problem so that employee turnover rates may not rise.
It may recommend increasing employee engagement, improving training and development programs, or providing better compensation and benefits. By using prescriptive analytics, HR professionals can take proactive steps to optimize their workforce and achieve their business goals.
HR analytics, also known as people analytics, is the process of using data and analytical methods to gain insights and make informed decisions about human resources within an organization. It involves collecting and analyzing data related to employees’ performance, engagement, recruitment, retention, training, and other HR processes.
In practice, HR analytics involves several steps and considerations:

1.Define the objectives: Clearly identify the goals and objectives you want to achieve through HR analytics. This could include improving employee productivity, reducing turnover, enhancing recruitment processes, or identifying skills gaps.
2. Data collection: Gather relevant data from various sources such as HR systems, performance management software, employee surveys, and external sources. This data may include employee demographics, performance metrics, training records, engagement surveys, and more.
3. Data preparation: Clean and organize the collected data, ensuring it is accurate and reliable. This may involve data cleaning, data integration, and data transformation to make it suitable for analysis.
4. Data analysis: Apply analytical techniques to uncover patterns, correlations, and insights within the data. This could involve statistical analysis, data visualization, and predictive modeling. Examples of analysis might include identifying factors that contribute to high employee turnover, predicting future workforce needs, or determining the impact of training programs on performance.
5. Interpretation and insights: Analyze the results of the data analysis and extract meaningful insights. These insights can help HR professionals make data-driven decisions and recommendations to improve HR processes and outcomes.
6. Communicate findings: Present the findings and insights in a clear and concise manner to stakeholders, such as HR managers, senior leaders, and department heads. Use visualizations and storytelling techniques to effectively communicate the results and their implications.
7. Action planning and implementation: Develop action plans based on the insights gained from the analytics. Collaborate with relevant stakeholders to implement changes or interventions based on the findings. This could involve modifying recruitment strategies, redesigning training programs, or adjusting performance management processes.
8. Monitor and evaluate: Continuously track the impact of the implemented changes and monitor key HR metrics. Evaluate the effectiveness of the interventions and make adjustments as needed.
It’s important to note that HR analytics is an ongoing process, and organizations should develop a culture of data-driven decision-making to maximize the benefits. Additionally, it’s crucial to ensure data privacy and compliance with relevant regulations when collecting and analyzing employee data.
What is the difference between descriptive and diagnostic analytics?
Descriptive analytics involves analyzing historical data to identify patterns and trends, while diagnostic analytics further identifies the underlying causes of workforce issues.
How many types of HR analytics are there?
There are four types of HR analytics. These four types of HR analytics are descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics. Each of these different types of HR analytics has its own unique purpose and can help HR professionals address specific workforce issues.
How does predictive analytics differ from prescriptive analytics?
Predictive analytics involves using data to make predictions about future workforce trends, while prescriptive analytics goes beyond prediction to suggest specific courses of action to address those trends.
How can HR professionals use descriptive analytics?
HR professionals can use descriptive analytics to gain an understanding of what has happened in the past, such as employee turnover rates or workforce demographics, and identify areas for improvement.
What are the benefits of using diagnostic analytics?
Diagnostic analytics can help HR professionals identify the root causes of workforce issues, such as high turnover rates, and develop effective solutions to address those issues.
How can prescriptive analytics help HR professionals optimize their talent management strategies?
Prescriptive analytics can suggest specific courses of action to help HR professionals optimize their talent management strategies, such as improving training and development programs, providing better compensation and benefits, or increasing employee engagement. By using prescriptive analytics, HR professionals can take proactive steps to achieve their business goals.
In conclusion, HR analytics is a powerful tool for HR professionals, enabling them to make informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
There are four types of HR analytics – descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive.
These four types of HR analytics can provide HR professionals with valuable insights into their workforce, help them identify areas for improvement, and ultimately drive business success.
By using the different types of HR analytics, HR professionals can optimize their talent management strategies, improve employee engagement and retention, and develop effective solutions to address workforce issues. As HR analytics continues to evolve and become more sophisticated, it will become an increasingly important tool for organizations to achieve their business objectives and compete in a rapidly changing business environment.
© 2007-2025 CHRMP| All Rights Reserved | Powered by Ripples Learning & Research Private Limited

Fill in the below details to get a CHRMP HR Analytics Program Plan.
